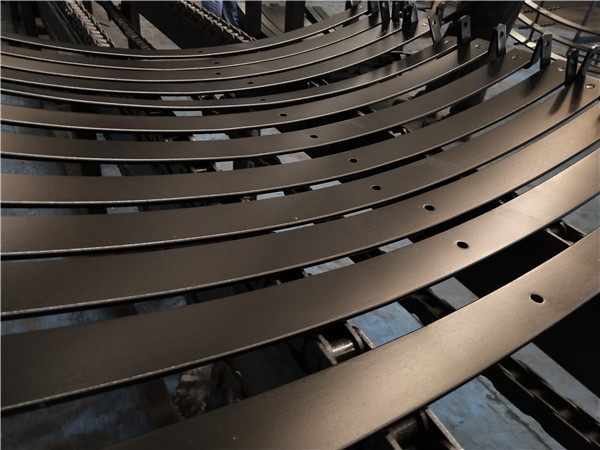
Leaf springs are an integral part of a vehicle’s suspension system, providing support and stability. In order to withstand the constant stress and pressure they endure, leaf springs need to be hardened and tempered to ensure their durability and longevity. Hardening and tempering are two essential processes that are used to strengthen the material and improve its mechanical properties. In this article, we will explore the techniques of quenching, tempering, and their application in the hardening and tempering of leaf springs.
Quenching is a process that involves heating the material to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it in a liquid medium, such as water or oil. This rapid cooling causes the material to harden, increasing its strength and toughness. When it comes to leaf springs, quenching is commonly used to increase the hardness of the steel, making it more resistant to wear and fatigue. The specific quenching process used for leaf springs depends on the composition of the steel and the desired mechanical properties.
After the quenching process, the material becomes extremely hard and brittle. In order to reduce this brittleness and improve the material’s toughness, tempering is carried out. Tempering involves reheating the quenched material to a lower temperature and then cooling it at a slower rate. This process allows the internal stresses within the material to be relieved, resulting in a more ductile and less brittle material. Tempering also helps to improve the material’s resistance to impact and shock loading.
The hardening and tempering process for leaf springs begins with the selection of the appropriate steel alloy. Commonly used steel alloys for leaf springs include 5160, 9260, and 1095. These alloys are chosen for their high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and ability to withstand heavy loads. Once the steel is selected, it is heated to a specific temperature based on the alloy composition and then quenched in an appropriate medium to achieve the desired hardness.
Following quenching, the material is then tempered to the required strength and toughness. The tempering temperature and duration are carefully controlled to achieve the desired mechanical properties, such as hardness, strength, and ductility. The final result is a leaf spring that is strong, flexible, and able to withstand the rigors of heavy-duty applications.
Hardening and tempering of leaf springs is a critical process that requires precision and expertise. Improper quenching and tempering can lead to a variety of issues, such as cracking, warping, or inadequate hardness. Therefore, it is essential to follow industry best practices and adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure that the leaf springs meet the necessary specifications.
In conclusion, the hardening and tempering of leaf springs play a crucial role in ensuring their performance and longevity. The combination of quenching and tempering processes results in a material that is both hard and tough, making it well-suited for the demanding conditions that leaf springs are subjected to. By understanding the techniques of quenching and tempering and their application in the hardening and tempering of leaf springs, manufacturers can produce high-quality, reliable leaf springs that meet the needs of various automotive and industrial applications.
Post time: Dec-11-2023