A leaf spring is the most widely used elastic element in automobile suspension. It is an elastic beam with approximately equal strength composed of several alloy spring leaves of equal width and unequal length. It bears the vertical force caused by the dead weight and load of the vehicle and plays the role of shock absorption and cushioning. At the same time, it can also transfer the torque between the vehicle body and the wheel and guide the wheel trajectory.
In the use of vehicles, in order to meet the requirements of different road conditions and load changes, it is inevitable to increase or decrease the number of leaf springs of the vehicle.
The increase or decrease of the number of leaf springs will have a certain effect on its stiffness and service life. Following are concerned introduction and analysis about this effect.
(1) The calculation formula of conventional leaf spring stiffness C is as follows:
The parameters are described below:
δ:Shape factor (constant)
E:Elastic modulus of material (constant)
L:The function length of the leaf spring;
n:Number of spring leaves
b:Width of the leaf spring
h:Thickness of each spring leaf
According to the above-mentioned stiffness (C) calculation formula, the following conclusions can be drawn:
The leaf number of leaf spring assembly is proportional to the rigidity of the leaf spring assembly. The more the leaf number of leaf spring assembly, the greater the rigidity ; the less the leaf number of leaf spring assembly, the lower the rigidity .
(2) Drawing design method of each leaf length of leaf springs
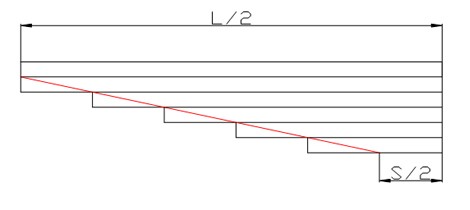
When designing the leaf spring assembly, the most reasonable length of each leaf is shown in Figure 1 below:
(Figure 1.Reasonable design length of each leaf of leaf spring assembly)
In the figure1, L / 2 is the half length of the spring leaf and S / 2 is the half length of the clamping distance.
According to the design method of the leaf spring assembly length, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1) The increase or decrease of the main leaf has a corresponding increase or decrease relationship on the stiffness of the leaf spring assembly, which has little effect on the force of other leaves, and will not have a bad effect on the service life of the leaf spring assembly.
2) The increase or decrease of the non-main leaf will affect the rigidity of the leaf spring assembly and at the same time have a certain effect on the service life of the leaf spring assembly.
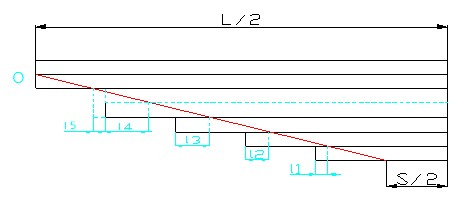
① Increase a non-main leaf of leaf spring assembly
According to the drawing design method of the leaf spring, when the non-main leaf is added, the slope of the red line that determines the length of the leaves will become larger after being drawn from the O point. In order to make the leaf spring assembly play an ideal role, the length of each leaf above the increased leaf should be correspondingly lengthened; the length of each leaf below the increased leaf should be shortened correspondingly. If a non-main leaf spring is added at will, other non-main leaves will not perform their due function well, which will affect the service life of the leaf spring assembly.
As shown in Figure 2 below. When the third non-main leaf is added, the corresponding the third leaf shall be longer than the original third leaf , and the length of other non-main leaves shall be reduced accordingly, so that each leaf of leaf spring assembly can play its due role.
(Figure 2. Non-main leaf added to leaf spring assembly)
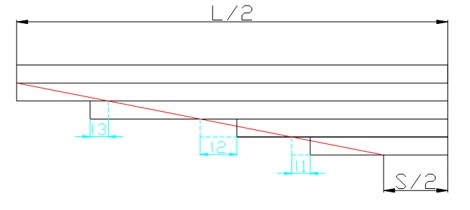
② Decrease a non-main leaf of leaf spring assembly
According to the drawing design method of the leaf spring, when reducing the non-main leaf, the red line that determines the length of the leaves is drawn from the O point and the slope becomes smaller. In order to make the leaf spring assembly play an ideal role, the length of each leaf above the reduced leaf should be reduced accordingly; the length of each leaf below the reduced leaf should be increased accordingly; so as to give the best play to the role of materials. If a non-main leaf is reduced at will, other non-main leaves will not perform their due function well, which will affect the service life of the leaf spring assembly.
As shown in Figure 3 below. Reduce the third non-main leaf, the length of the new third leaf shall be shorter than the original third leaf , and the length of other non-main leaves shall be correspondingly lengthened, so that each leaf of the leaf spring assembly can play its due role.
Figure 3. Non-main leaf decreased from leaf spring assembly)
Through the analysis of stiffness calculation formula and leaf spring drawing design method, the following conclusions can be drawn:
1) The number of spring leaves is directly proportional to the stiffness of leaf springs.
When the width and thickness of the leaf spring remain unchanged, the more the number of spring leaves, the greater the stiffness of the leaf spring assembly; the less the number , the smaller the stiffness .
2) In the case that the leaf spring design has been completed, adding the main leaf has no effect on the service life of the leaf spring assembly, the force of each leaf of leaf spring assembly is uniform, and the material utilization rate is reasonable.
3) In the case that the leaf spring design has been completed, increasing or decreasing the non-main leaf will have an adverse effect on the stress of other leaves and the service life of leaf spring assembly. The length of other leaves shall be adjusted at the same time when increasing or decreasing the number of spring leaves.
For further news, please visit www.chleafspring.com.
Post time: Mar-12-2024